
Sets the host key to a static initial value for this stanza.
You can use the following settings in both monitor and batch input stanzas. splunk _internal call /services/data/inputs/monitor/_reload -auth
#Splunk universal forwarder inputs.conf install
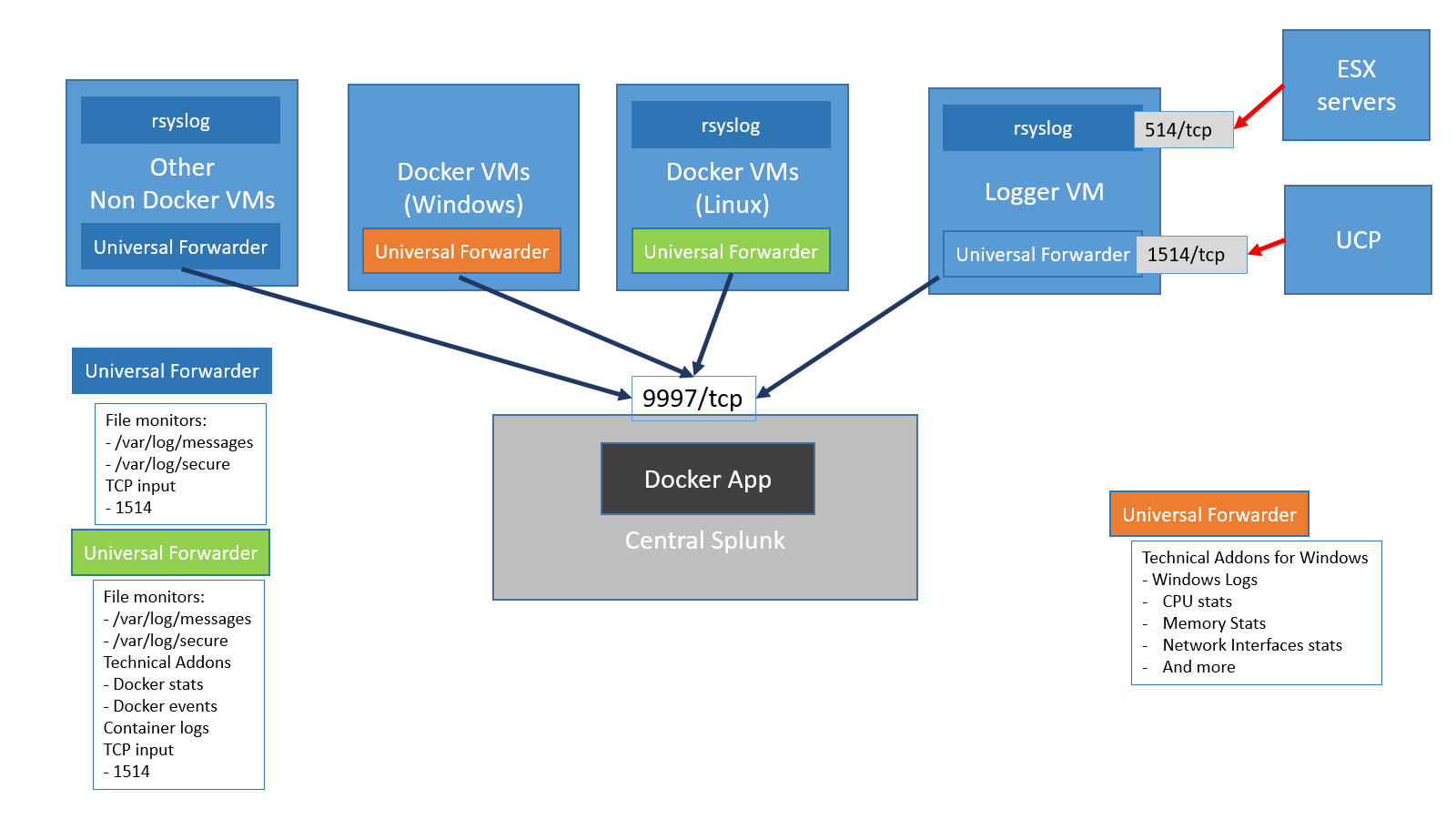
Install the Splunk Cloud Platform universal forward credentials package onto the machine.Ĭonfigure file monitoring with nf.Install a universal forwarder on the machine that you want to collect the AD data.If you want to send Active Directory (AD) data to Splunk Cloud Platform, you must install and configure a forwarder before you begin making edits to configuration files on the forwarder.

You can find the defaults for settings in the $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/default/nf directory.įor more information about configuration files, see About configuration files in the Splunk Enterprise Admin Manual.Ĭonfigure a forwarder to send data to Splunk Cloud Platform If you don't specify a value for a setting, the Splunk platform uses the default for that setting. You can configure multiple settings in an input stanza. To learn more about the nf file, see nf in the Splunk Enterprise Admin Manual. These locations are on the machine that runs Splunk Enterprise or the forwarder. To configure an input, add a stanza to the nf file in the $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local/ directory or your own custom application directory in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/. If you use Splunk Cloud Platform, you can use either Splunk Web or a forwarder to configure file monitoring inputs. The nf file provides the most configuration options for setting up a file monitor input. You can use the nf file to monitor files and directories with the Splunk platform. For more details on using the CLI in general, see Administer Splunk Enterprise with the CLI in the Splunk Enterprise Admin Manual.Monitor files and directories with nf You can choose to edit the configuration files through the command line. The forwarder writes configurations for forwarding data to nf in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local/).Įdit the configuration files through the command line This prevents typos and other mistakes that can occur when you edit configuration files directly. When you make configuration changes with the CLI, the universal forwarder writes the configuration files.

You can edit them however you normally edit files, such as through a text editor or the command line, or you can use the Splunk Deployment Server.

Navigate to nf in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local/ to locate your Universal Forwarder configuration files. Optionally edit the Universal forwarder configuration files to further modify how your machine data is streamed to your indexers. Configure the universal forwarder using configuration files


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
